
Joanna Syrda, University of Bath
The best marriages are probably based on teamwork. But it seems individual contributions do matter – specifically, who earns how much of the household income.
My research shows that in, heterosexual couples, men are happier when both partners contribute financially – but much prefer to be the main breadwinners.
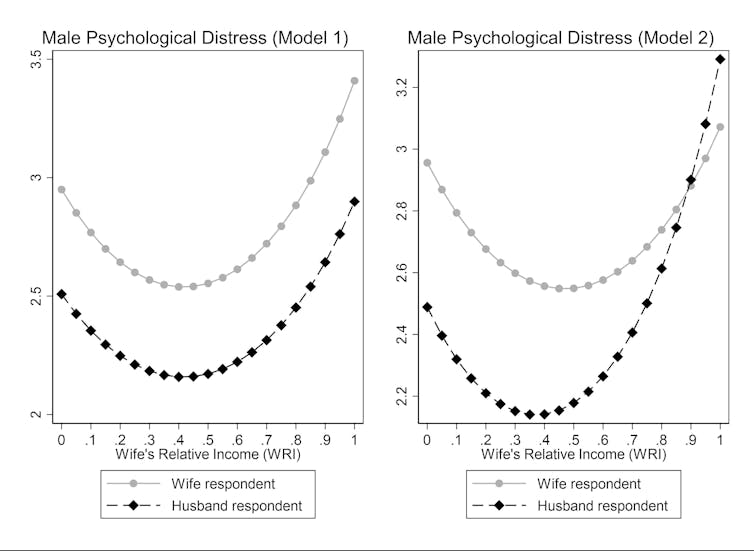
With stress levels high when they are sole breadwinners, men appear to be more relaxed when their wives or partners earn anything up to 40% of the household income.
But their distress levels increase sharply as their spouse’s wages rise beyond that point. And they find it most stressful when they are entirely economically dependent on their partners.
The findings are based on an analysis of over 6,000 married or cohabiting heterosexual couples over a period of 15 years. Levels of distress are calculated based on feeling sad, nervous, restless, hopeless, worthless, or that day to day life is an effort.
Men who are the only earners are relatively unhappy but they were not as stressed as men whose partners are the principal earners. Neither of the extreme scenarios is good for male mental health.
The exception is men who knowingly partner with a high-earning woman. These men do not appear to suffer from higher psychological distress when their partners earn more. People do not pick their partners at random, so if the woman was the higher earner before marriage, then the potential income gap was already clear to the man – perhaps even a reason to partner with them.
Balance of power
There are a variety of reasons which may explain why husbands who are “outearned” by their partners may suffer from psychological distress.
When one person in a couple earns a much greater proportion of the joint income, it may create a relationship imbalance. For example, if the relationship deteriorates significantly, the possibility of divorce or separation can make the lower earner feel more vulnerable, financially speaking. These effects are larger among cohabiting couples, possibly due to the higher probability of break up.
Even if breaking up is not on the cards, money that comes into the household predominantly through one partner also affects the balance of power. This is important if partners have a different view on what is best for their family, how much to save, what to spend their money on, and various plans and big decisions.
Traditional gender identity norms
Another theory involves the historic effect of social, psychological and cultural norms when it comes to gender roles. The social construct of a male breadwinner has been highly durable in the past.
For generations, in many cultures, there has been an expectation that men will be the primary income provider in the family, and masculinity is highly linked to fulfilling this expectation. Faced with a change in this outcome by being outearned by their partners, means men are likely to experience high levels of psychological distress.
But the reality is that things are changing. In places like the US, the percentage of wives outearning their husbands is growing. In 1980, only 13% of married women earned about as much or more than their husbands. In 2000, that figure almost doubled to 25%, and in 2017 it was 31%. This trend is likely to continue into the future and similar patterns have been observed in other countries.
The stress of being a sole bread winner
On average, men in my study said they experienced the lowest levels of psychological distress when their partners earned no more than 40 percent of household income.
But for men, being the sole breadwinner may also come at a psychological price. For even if social gender norms support this situation, being the only income earner in a household comes with a lot of responsibility and pressure and so may result in significant anxiety and distress.
And while the emerging profile of a female breadwinner and its possible consequences has been widely researched, very little attention has been devoted to the psychological hurdles faced by male primary breadwinners.
This lack of research is perhaps symptomatic of the strength of the male bread-winning tradition. Health and wellbeing research is typically devoted to new phenomena, rather than widely accepted norms in society.
Gender identity norms clearly still induce a widely held aversion to a situation where the wife earns more than her husband. And as the number of women outearning their male partners grows, the traditional social norm of the male breadwinner may begin to adjust.
Joanna Syrda, Lecturer in Business Economics, University of Bath
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

